Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome Types
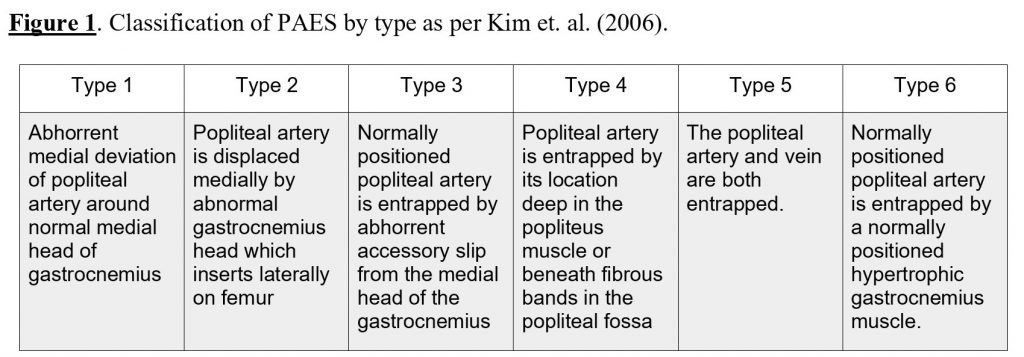
Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome types. The role of early diagnosis and. Type V occurs when the popliteal vein is entrapped with the popliteal artery in any of the above scenarios. From the perspective of anatomy PAES can be classified into five types.
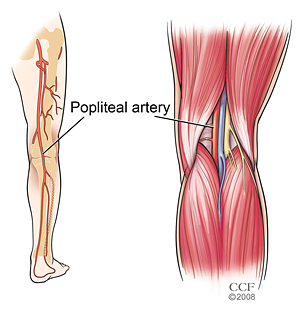
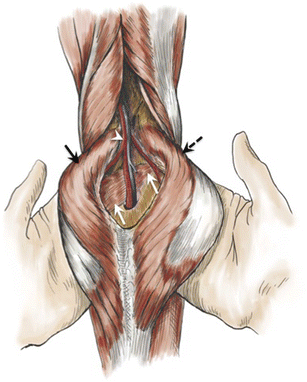
PAES occurs when nearby tendons and muscles squeeze or compress the popliteal artery. The popliteal artery is the main artery that runs through and behind the knee. Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome is a condition commonly found in young males preferably in the age group of 20 to 40 years.
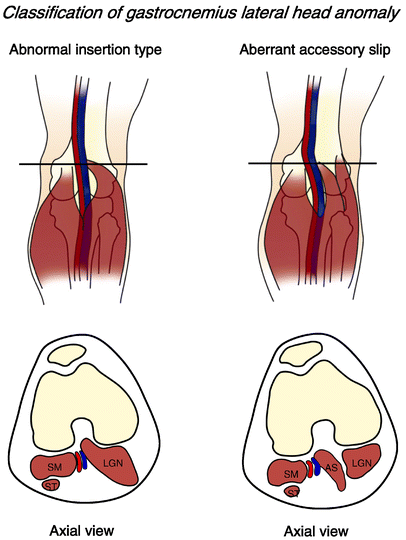
Popliteal artery entrap-ment syndrome. Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome usually the gastrocnemius muscle is caused by abnormalities in the calf muscles. Type II entrapment involves disruption.
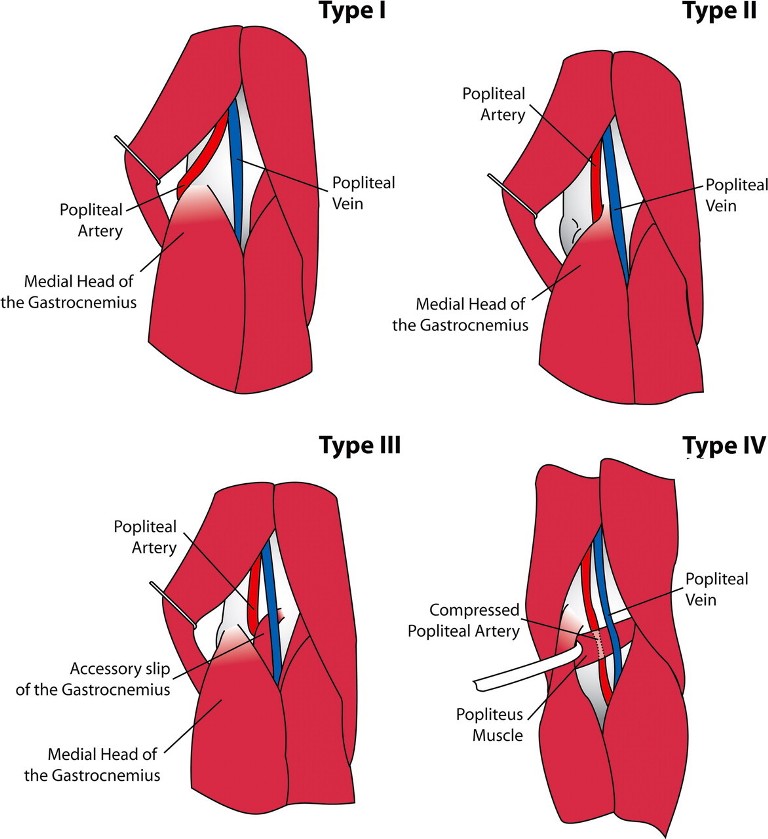
Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome PAES described by Stuart in1879 is an uncommon limb-threatening vascular entity comprising approximately 017-35 of the general population in the United States US. The popliteal artery may be compressed behind the knee due to congenital deformity of the muscles or tendon insertions of the popliteal fossa. Type 1 This type occurs because of an abnormal relationship of the popliteal artery with the medial head of gastrocnemius MHG.
The types I and IV of the popliteal artery entrapment syndrome were found in one case type II in two cases type III in 4 cases while in one case a type of syndrome had not to be identified. A case series with variable timing of. Foot numbness and paresthesias also common.
The disease may begin at birth congenital or develop later acquired in life. Treatment should be performed as soon as possible as to avoid this course and the eventual necessity of interposition or bypass grafting. Type I entrapment is caused by the popliteal artery forming prior to the migration of the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle.
Functional Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome Continuous popliteal artery compression leads to its progressive fibrosis which may cause thrombosis or post-stenotic aneurysmal dilation. Mustapha JA Saab F Danielson K et al.
The popliteal artery may be compressed behind the knee due to congenital deformity of the muscles or tendon insertions of the popliteal fossa.
Popliteal artery entrap-ment syndrome. Due to an abnormal course of the popliteal artery and the calf muscle group the artery can be compressed and reduce blood flow. A current interpretation of popliteal vascular entrapment. Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome PAES occurs when muscles that surround the popliteal artery in the area of the popliteal fossa occlude the artery and sometimes the vein as well and decrease blood flow to the lower leg. Foot numbness and paresthesias also common. Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. Popliteal artery entrap-ment syndrome. From the perspective of anatomy PAES can be classified into five types. Type 1 This type occurs because of an abnormal relationship of the popliteal artery with the medial head of gastrocnemius MHG.
The types I and IV of the popliteal artery entrapment syndrome were found in one case type II in two cases type III in 4 cases while in one case a type of syndrome had not to be identified. The most common types of the syndrome were those caused by an abnormal medial head of the gastrocnemius type II n 35 4023 and aberrant course of the popliteal artery type I. Normal course of the popliteal artery at the back of the knee The popliteal artery entrapment syndrome is a rather uncommon pathology which results in claudication and chronic leg ischemia. Type I entrapment is caused by the popliteal artery forming prior to the migration of the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle. Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome usually the gastrocnemius muscle is caused by abnormalities in the calf muscles. The popliteal artery is the main artery that runs through and behind the knee. The types I and IV of the popliteal artery entrapment syndrome were found in one case type II in two cases type III in 4 cases while in one case a type of syndrome had not to be identified.

































Post a Comment for "Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome Types"